
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Electronics, and Center for Quantum Information Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
3 e-mail: chenziyang@pku.edu.cn
4 e-mail: luobin@bupt.edu.cn
5 e-mail: hongguo@pku.edu.cn
High-precision time interval measurement is a fundamental technique in many advanced applications, including time and distance metrology, particle physics, and ultra-precision machining. However, many of these applications are confined by the imprecise time interval measurement of electrical signals, restricting the performance of the ultimate system to a few picoseconds, which limits ultrahigh precision applications. Here, we demonstrate an optical means for the time interval measurement of electrical signals that can successfully achieve femtosecond (fs) level precision. The setup is established using the optical frequency comb (OFC) based linear optical sampling (LOS) technique to realize timescale-stretched measurement. We achieve a measurement precision of 82 fs for a single LOS scan measurement and 3.05 fs for the 100-times average with post-processing, which is three orders of magnitude higher than the results of older electrical methods. The high-precision time interval measurement of electrical signals can substantially improve precision measurement technologies.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(12): 2222
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院, 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
涡旋光束的轨道角动量 (OAM) 可用于信息的编码, 因此在自由空间光通讯等领域具有重要的应用价值。然而, 实际的传输空间通常存在着各种随机介质, 会造成传输涡旋光束的波面畸变, 导致传统的方法无法准确测量涡旋光束的轨道角动量。针对此问题, 以毛玻璃作为随机介质, 基于深度学习技术, 从涡旋光束经过毛玻璃所产生的散斑场中准确识别出了涡旋光束的轨道角动量。为提升光信息的编码与传输能力, 还进一步测试了多涡旋结构光束的轨道角动量识别。测试结果表明, 对于五个涡旋结构的光束, 所设计的网络仍能从单帧散斑图中准确识别其轨道角动量。
量子光学 轨道角动量 深度学习 涡旋光束 散斑 quantum optics orbital angular momentum deep learning vortex beam speckle
1 华侨大学 信息科学与工程学院 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室,福建 厦门 361021
2 闽南师范大学 物理与信息工程学院,福建 漳州 363000
不同于毛玻璃等固态散射介质静止不变的特点,浑浊介质对光束的散射作用同时体现在空间及时间上,当浑浊介质动态变化时,大多数的传统散射成像方法失效。针对以上问题,文中采用了一种基于深度学习恢复散斑图像的方法,研究了浑浊介质中,不同散射介质及散射介质浓度不同的条件下,神经网络的图像恢复效果,并利用不同浓度散射介质获得的散斑图像混合训练测试神经网络的泛化能力。实验结果表明,在不同散射介质及散射介质浓度不同的条件下,该网络均能够根据散斑图像获得较高保真度的恢复图像,且在不同浓度散射介质的散斑图像混合训练的情况下,网络泛化能力及鲁棒性强。
图像恢复 散射介质 散射成像 深度学习 image reconstruction scattering medium scattering imaging deep learning 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(8): 20220215
南京航空航天大学材料科学与技术学院,江苏省高效电化学储能技术重点实验室,南京 211106
锂离子电容器一个电极采用电池型负极,一个采用电容型正极,因而兼具高能量密度、高功率密度的优点,有望成下一代新型储能器件。基于Faraday反应的电池型电极与电容型电极动力学不匹配是锂离子电容器的一个巨大挑战,因此研究者们发展了多种倍率性锂离子电池材料。在这些材料中,钒基材料以其成本低、比容量大、倍率性能优异等优点被认为是锂离子电容器的理想负极材料。综述了包括Li3VO4、VN、Li3V2O5在内的多种不同类型钒基锂离子电池材料的储锂机理与性能优化的研究进展,并展望了锂离子电容器中钒基负极材料的发展方向。
锂离子电容器 负极 钒酸锂 氮化钒 锂钒氧化物 lithium-ion capacitors anode materials lithium vanadate vanadium nitride lithium vanadium oxide
1 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室,华侨大学信息科学与工程学院,福建 厦门 361021
2 华侨大学工学院,福建 泉州 362021
白光扫描干涉测量中,频域分析(FDA)方法通过波数域的相位解包裹和线性拟合得到斜率来计算物体表面形貌,干涉仪中的振动噪声和背景噪声会给斜率测量带来误差,从而影响FDA方法的测量精度。研究发现,波数域相位线性拟合后的常数项能够有效补偿噪声对FDA方法的影响,波数域相位补偿(PCWD)方法通过对波数域的线性相位作傅里叶逆变换,得到空域的振幅和相位分布,以距离振幅最高点最近的相位零点测量光滑反射镜表面形貌。仿真结果表明:存在振动噪声时,PCWD方法有90%的概率补偿FDA测量结果中平均8.9 nm的误差,也有10%的概率给FDA测量结果额外引入平均1.9 nm的误差;存在背景噪声时,FDA与PCWD方法的平均测量误差分别为4.5 nm和0.6 nm。实验结果表明:FDA方法测量的反射镜表面结构的起伏小于25 nm,重复率为7.4 nm;PCWD方法测量的反射镜表面结构的起伏小于4 nm,重复率为1.1 nm。综上所述,PCWD方法在FDA方法的基础上进一步提升了测量精度。
测量 白光干涉 表面检测 相位补偿 噪声抑制 中国激光
2022, 49(11): 1104002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Physical Science and Technology, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
The spatial rogue waves (RWs) generated by a wide Gaussian beam in a saturated nonlinear system are experimentally observed. Our observations show that RWs are most likely to occur when Gaussian light evolves to the critical state of filament splitting, and then the probability of RWs decreases with voltage fluctuations. The occurrence probability of RWs after splitting is related to the nonlinear breathing phenomenon of optical filament, and the statistics of RWs satisfy the long-tailed L-shaped distribution. The experiment proves that the presence of high-frequency components and the aggregation of low-frequency components can serve as a prerequisite for the occurrence of extreme events (EEs).
optical rogue waves spatial rogue waves saturable nonlinearity Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(8): 081901
1 Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi, 221005, India
2 Department of Mining Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi, 221005, India
3 College of Information Science and Engineering, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Light Propagation and Transformation, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, Fujian 361021, China
Correlation holography uses incoherent light to reconstruct holograms. This technique reconstructs objects as distributions of two-point coherence function rather than using optical fields, as in conventional holography. The basic principle of correlation holography is derived from the van Cittert--Zernike theorem and relies on the similarity between the optical field and the coherence functions. Experimental implementation of the correlation holography techniques requires a field or intensity interferometer, and fringe analysis and cross-covariance measurement in these interferometers require a conventional camera with array detectors. With the availability of digitally controlled diffractive elements, it is possible to replace the incoherent light source, such as a rotating ground glass, with a digital source loaded with the random patterns in sequence. Such strategies ease the burden on the detector and allow for correlation holography with a single-pixel detector (SPD) to be used. This review paper discusses a close connection between digital holography and correlation holography. The principles of correlation holography with the SPD are reviewed in detail, and the advantages of using digital sources to mimic incoherent illumination in the correlation holography are examined in the context of three-dimensional and complex field imaging.
imaging systems correlation holography single-pixel detector digital holography coherence optics phase recovery 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(10): 1011011
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院, 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
由于随机散射效应,相干光束经过强散射介质后,出射光场变成光强呈无序分布的散斑场,因此无法直接从出射场获取入射光的信息。然而,在随机散射过程中,出射散斑场仍然携带着入射光场信息。从散斑场中获取原始信息以实现物体的重建是一个备受关注的研究课题。研究人员针对该问题提出了包括散斑相关、传输矩阵、波前调控及时间反演与相位共轭等技术。着重介绍了基于相关全息原理的散射成像技术,主要包括其原理、发展历史以及最新的研究进展,并对该技术的未来发展趋势进行了展望。
成像系统 散射成像 相关全息 散射介质 散斑场 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(2): 0200001
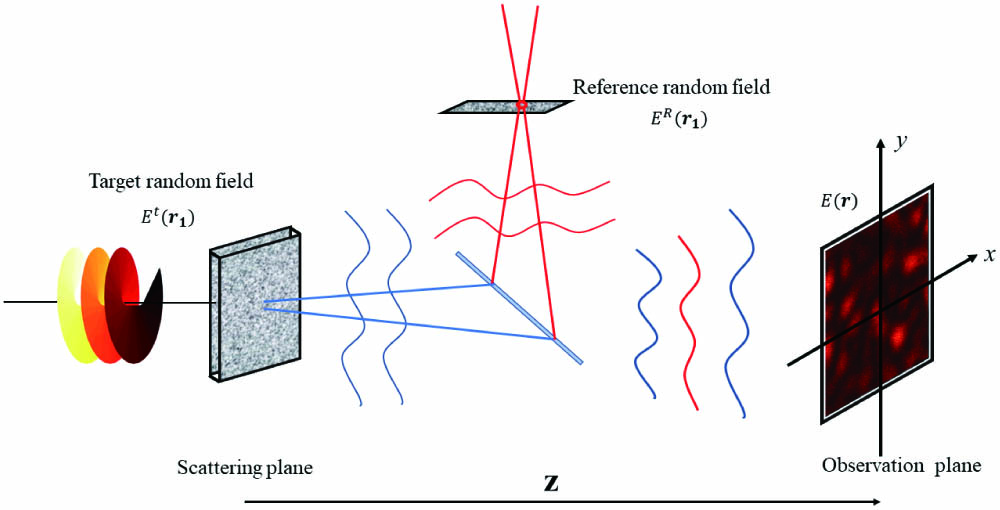
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Science and Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China
2 Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005, Uttar Pradesh, India
3 CREOL, College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32816-2700, USA
4 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Light Propagation and Transformation, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China
Encoding information using the topological charge of vortex beams has been proposed for optical communications. The conservation of the topological charge on propagation and the detection of the topological charge by a receiver are significant in these applications and have been well established in free-space. However, when vortex beams enter a diffuser, the wavefront is distorted, leading to a challenge in the conservation and detection of the topological charge. Here, we present a technique to measure the value of the topological charge of a vortex beam obscured in the randomly scattered light. The results of the numerical simulations and experiments are presented and are in good agreement. In particular, only a single-shot measurement is required to detect the topological charge of vortex beams, indicating that the method is applicable to a dynamic diffuser.
intensity correlation vortex beam scattering Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(2): 022603
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院, 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
介绍了激光光束经过湍流大气以及散射介质的传输特性。当激光在湍流大气中传输时, 湍流大气的扰动会影响光束的传输特性。此时, 激光光束仍然保持光束的特性, 因此可以应用扩展的 Huygens-Fresnel 衍射积分研究激光在湍流大气中的传输特性。研究表明, 当光束在湍流大气中传输时, 光束的光斑大小、偏振态、空间相干度、闪烁因子等参数发生了变化。这些参数的变化除了与大气湍流性质有关外, 还与光束的特性有关。因此选择合适的入射光束可以减低湍流大气对光束传输的影响。当相干激光经过散射介质后, 会呈现散斑。通过调控入射激光的波前, 可以使得激光经过散射介质后聚焦。介绍了实现激光经过散射介质聚焦的技术, 包括基于迭代反馈的波前整形技术、传输矩阵, 以及数字相位共轭技术等。最后, 展望这些技术应用于激光在实际大气中的传输, 实现激光穿云透雾的目标。
激光技术 湍流大气 散射介质 激光光束 传输 波前调控技术 aser technology turbulent atmosphere scattering medium laser beam propagation wavefront shaping





